New research shared with The New York Times estimates the extent to which rising home insurance premiums, driven higher by climate change, are cascading into the broader real estate market and eating into home values in the most disaster-prone areas.
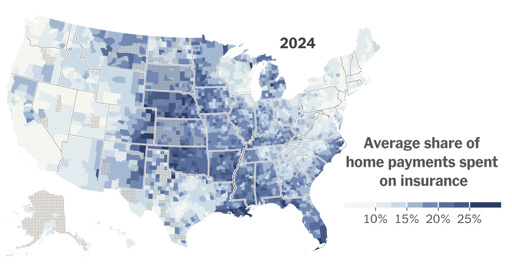
The study, which analyzed tens of millions of housing payments through 2024 to understand where insurance costs have risen most, offers first-of-its-kind insight into the way rising insurance rates are affecting home values.
Since 2018, a financial shock in the home insurance market has meant that homes in the ZIP codes most exposed to hurricanes and wildfires would sell for an average of $43,900 less than they would otherwise, the research found. They include coastal towns in Louisiana and low-lying areas in Florida.
Changes in an under-the-radar part of the insurance market, known as reinsurance, have helped to drive this trend. Insurance companies purchase reinsurance to help limit their exposure when a catastrophe hits. Over the past several years, global reinsurance companies have had what the researchers call a “climate epiphany” and have roughly doubled the rates they charge home insurance providers.
After analyzing 74 million home payments — which included mortgage, taxes and insurance and were made between 2014 and 2024 — the researchers found that a rapid repricing of disaster risk had been responsible for about a fifth of overall home insurance increases since 2017. Another third could be explained by rising construction costs.
The researchers estimated the effects of the reinsurance shock on home prices in the ZIP codes most vulnerable to catastrophes. They found that rising insurance premiums weighed down home values by about $20,500 in the top 25 percent of homes most exposed to catastrophic hurricanes and wildfires, and by $43,900 in the top 10 percent.